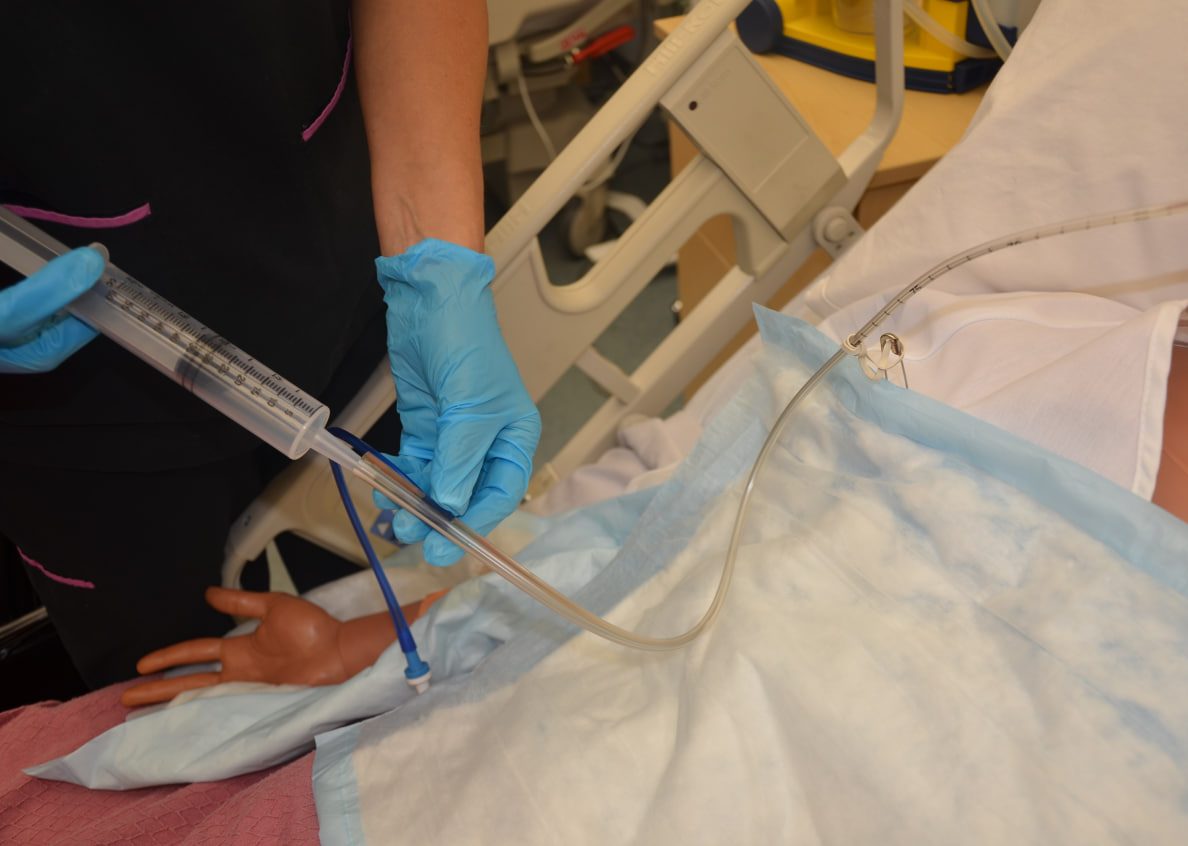
Nasogastric (NG) tubes are thin, flexible tubes inserted through the nose and down into the stomach.
Contents
They provide a way to deliver liquid nutrition to patients who are unable to eat safely or adequately by mouth. This can be due to various reasons, including:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Recovering from surgery
- Unconsciousness
If you’re tasked with feeding a patient through an NG tube, it’s crucial to follow proper procedures to ensure their safety and well-being. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you
Preparation:
- Gather Supplies: You’ll need:
- Prescribed feeding formula or liquid food
- Feeding bag or syringe
- NG tube
- Stethoscope (to check for proper tube placement)
- Water for flushing the tube
- Lubricating jelly (optional)
- Drainage bag (if applicable)
- Measuring cup or scale
- Clean towels or bib
- Wash Your Hands: Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Check for Doctor’s Orders: Review the doctor’s instructions regarding the type and amount of feeding formula, feeding rate, and any specific patient considerations.
- Prepare the Feeding Formula: Measure the prescribed amount of formula or liquid food. If using a pre-mixed formula, follow the instructions for preparation. Warm the formula to a comfortable temperature (usually body temperature) unless otherwise instructed by the doctor.
Feeding Procedure
- Position the Patient: Elevate the patient’s head and neck to at least a 30-degree angle to prevent aspiration (fluid entering the lungs).
- Verify Tube Placement: If you’re unsure about tube placement, consult a healthcare professional. Briefly listen for a whooshing sound in the stomach area with a stethoscope while gently injecting a small amount of air into the tube (as instructed by a healthcare professional).
- Administer Feeding:
- Using a feeding bag: Connect the feeding bag to the NG tube and adjust the flow rate as directed. Ensure the feeding bag is positioned lower than the patient’s stomach.
- Using a syringe: Fill the syringe with the formula and slowly push the plunger to administer the feeding.
- Flush the Tube: After feeding, flush the tube with a small amount of clean water to prevent clogging.
- Monitor the Patient: Observe for signs of discomfort like nausea, vomiting, or abdominal distention.
- Document the Feeding: Record the amount and type of formula fed, the feeding time, and any observations about the patient’s tolerance.
Additional Tips:
- Lubricate the nostrils (optional): Apply a small amount of lubricating jelly to the nostrils for easier tube insertion (consult a healthcare professional if unsure).
- Feed Slowly: Administer the feeding slowly to prevent stomach discomfort.
- Maintain Hygiene: Clean the feeding equipment and the patient’s surrounding area after each feeding.
Important Note:
This is a general guide. Always follow the specific instructions provided by the doctor or a qualified healthcare professional.
If you have any questions or concerns about feeding a patient through an NG tube, consult a healthcare professional immediately.